寒武纪成功适配DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp模型
2025年9月29日,寒武纪已同步实现对深度求索公司最新模型DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp的适配,并开源大模型推理引擎vLLM-MLU源代码。代码地址和测试步骤见文末,开发者可以在寒武纪软硬件平台上第一时间体验DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp的亮点。
寒武纪一直高度重视大模型软件生态建设,支持以DeepSeek为代表的所有主流开源大模型。借助于长期活跃的生态建设和技术积累,寒武纪得以快速实现对DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp这一全新实验性模型架构的day 0适配和优化。
寒武纪一直重视芯片和算法的联合创新,致力于以软硬件协同的方式,优化大模型部署性能,降低部署成本。此前,我们对DeepSeek系列模型进行了深入的软硬件协同性能优化,达成了业界领先的算力利用率水平。针对本次的DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp新模型架构,寒武纪通过Triton算子开发实现了快速适配,利用BangC融合算子开发实现了极致性能优化,并基于计算与通信的并行策略,再次达成了业界领先的计算效率水平。依托DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp带来的全新DeepSeek Sparse Attention机制,叠加寒武纪的极致计算效率,可大幅降低长序列场景下的训推成本,共同为客户提供极具竞争力的软硬件解决方案。
↓ vLLM-MLU DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp适配的源码(点击文末“阅读原文”可直接跳转)↓
https://github.com/Cambricon/vllm-mlu
基于vLLM-MLU的DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp运行指南
一、环境准备
软件:需使用寒武纪训推一体镜像Cambricon Pytorch Container部署,镜像内预装运行vLLM-MLU的各项依赖。
硬件:4台8卡MLU服务器。
如需获取完整的软硬件运行环境,请通过官方渠道联系寒武纪。
二、运行步骤及结果展示
Step1:模型下载
模型文件请从Huggingface官网自行下载,后文用${MODEL_PATH}表示下载好的模型路径。
Step 2:启动容器
加载镜像,启动容器,命令如下:
# 加载镜像
docker load -i cambricon_pytorch_container-torch2.7.1-torchmlu1.28.0-ubuntu22.04-py310.tar.gz
# 启动容器
docker run -it --net=host
--shm-size'64gb'--privileged -it
--ulimitmemlock=-1${IMAGE_NAME}
/bin/bash
# 安装社区vLLM 0.9.1版本
pushd${VLLM_SRC_PATH}/vllm
VLLM_TARGET_DEVICE=empty pip install .
popd
# 安装寒武纪vLLM-mlu
pushd${VLLM_SRC_PATH}/vllm-mlu
pip install .
popd
Step 3:启动Ray服务
在执行模型前,需要先启动ray服务。启动命令如下:
# 设置环境变量
exportGLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=${INFERENCE_NAME}
exportNOSET_MLU_VISIBLE_DEVICES_ENV_VAR=1
# 主节点
ray start --head--port${port}
# 从节点
ray start --address='${master_ip}:${port}'
Step 4:运行离线推理
这里提供简易的离线推理脚本`offline_inference.py`:
importsys
fromvllmimportLLM, SamplingParams
defmain(model_path):
# Sample prompts.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature=0.6, top_p=0.95, top_k=20, max_tokens=10)
# Create an LLM.
engine_args_dict = {
"model": model_path,
"tensor_parallel_size":32,
"distributed_executor_backend":"ray",
"enable_expert_parallel":True,
"enable_prefix_caching":False,
"enforce_eager":True,
"trust_remote_code":True,
}
llm = LLM(**engine_args_dict)
# Generate texts from the prompts.
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
# Print the outputs.
foroutputinoutputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt:{prompt!r}, Generated text:{generated_text!r}")
if__name__ =='__main__':
main(sys[1])
运行如下命令,完成模型离线推理:
# 运行推理命令
pythonoffline_inference.py --model${MODEL_PATH}
运行结果符合预期,具体结果如下:

Step 5:运行在线推理
分别启动server和client,完成推理服务,示例如下:
# server
vllmserve${MODEL_PATH}
--port8100
--max-model-len40000
--distributed-executor-backend ray
--trust-remote-code
--tensor-parallel-size32
--enable-expert-parallel
--no-enable-prefix-caching
--disable-log-requests
--enforce-eager
# client, we post a single request here.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8100/v1/completions
-H"Content-Type: application/json"
-d'{"model":${MODEL_PATH},
"prompt": "The future of AI is",
"max_tokens": 50, "temperature": 0.7
}'
运行结果如下:
提取输入输出信息如下,符合预期。
Prompt:The futureofAIis Output:being shapedbya numberofkey trends. These include the riseoflargelanguagemodels, the increasing useofAIinenterprise, the developmentofmore powerfulandefficient AI hardware,andthe growing focusonAI ethicsandsafety. Largelanguagemodelsare
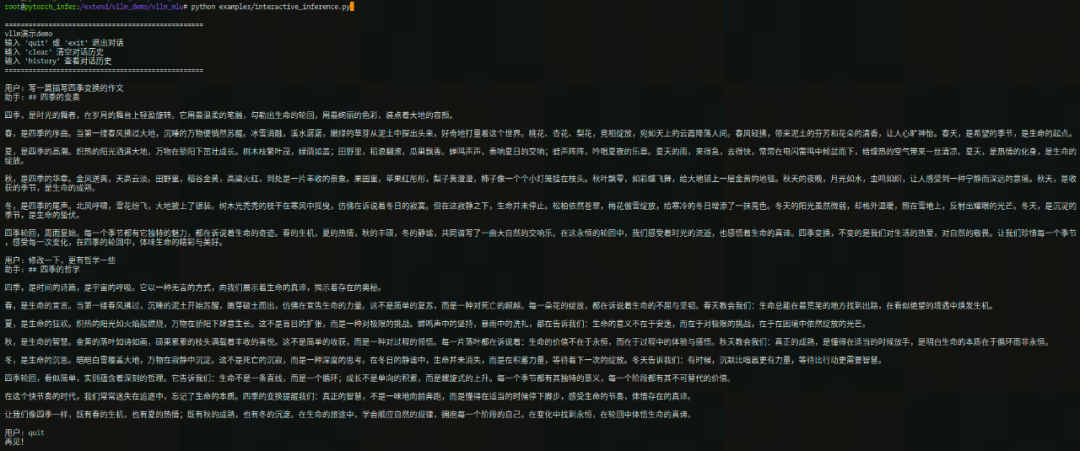
Step 6:运行交互式对话
使用vLLM-MLU框架,运行交互式对话demo,执行结果如下: